
In this study, we provide an automated assessment of the translation quality of Google Translate with human experts using sentiment and semantic analysis. In order to demonstrate our framework, we select the classic early twentieth-century novel ’The True Story of Ah Q’ with selected Mandarin Chinese to English translations. We use Google Translate to translate the given text into English and then conduct a chapter-wise sentiment analysis and semantic analysis to compare the extracted sentiments across the different translations. Our results indicate that the precision of Google Translate differs both in terms of semantic and sentiment analysis when compared to human expert translations. We find that Google Translate is unable to translate some of the specific words or phrases in Chinese, such as Chinese traditional idiomatic expressions. The mistranslations may be due to a lack of contextual significance and historical knowledge of China.
Xuechun Wang, Rodney Beard, Rohitash Chandra
Natural Language Processing Journal, Volume 13, December 2025, 100188
Used LLMs for sentiment and abuse analysis of Hollywood movie dialogues. Analyzed 1,000+ movie subtitles to track trends in emotion and abuse
Chandra, R., & Ren, G.
Machine Learning with Applications, Volume 22, December 2025, 100749

We present a machine learning framework to map the spatial distribution of minerals on Mars. Our framework utilises the Self-Organising Map and k-means clustering to identify clusters of spectral signatures of minerals.
Lovelock, Tejay, and Rohitash Chandra
Remote Sensing 17 (21) (2025) 3578 https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213578

We present a computational framework for analyzing anti-Hindu sentiment (Hinduphobia) during the COVID-19 period, introducing an abuse detection and sentiment analysis approach for longitudinal analysis on X.
Singh, A., & Chandra, R.
IEEE Access, vol. 13, pp. 175309-175335, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3617514

This study addresses this limitation by using semantic and sentiment analysis of selected LLMs for Indian languages, including Sanskrit, Telugu and Hindi. We select prominent texts (Bhagavad Gita, Tamas and Maha Prasthanam) that have been well translated by experts and use LLMs to generate their translations into English, and provide a comparison with selected expert (human) translations.
R. Chandra, A. Chaudhari and Y. Rayavarapu
IEEE Access, vol. 13, pp. 122386-122407, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3585629
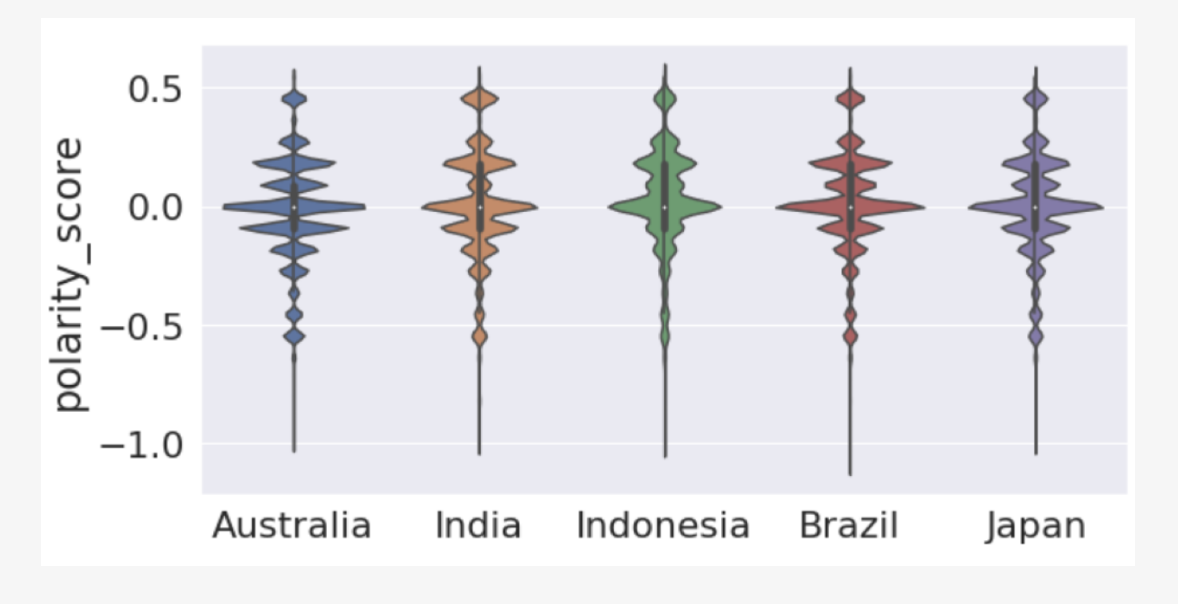
Anti-vaccine sentiments have been well-known and reported throughout the history of viral outbreaks and vaccination programmes. The COVID-19 pandemic caused fear and uncertainty about vaccines, which has been well expressed on social media platforms such as Twitter (X). We analyse sentiments from the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic and study the public behaviour on X during the planning, development, and deployment of vaccines expressed in tweets worldwide using a sentiment analysis framework via deep learning models. We provide visualisation and analysis of anti-vaccine sentiments throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. We review the nature of the sentiments expressed with the number of tweets and monthly COVID-19 infections. Our results show a link between the number of tweets, the number of cases, and the change in sentiment polarity scores during major waves of COVID-19. We also find that the first half of the pandemic had drastic changes in the sentiment polarity scores that later stabilised, implying that the vaccine rollout impacted the nature of discussions on social media.
Rohitash Chandra, Jayesh Sonawane, Jahnavi Lande
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2024, 8(12), 186; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc8120186

Hinduism seeks to provide insight into the nature of the universe and is not antithetical to science. Rohitash Chandra explains why he sees value in bringing together science and spirituality in the quest for knowledge. – “I envision a world where we are fearless in bringing science and religion (spirituality) together. Hinduism is built on the philosophical foundations of the search for the truth and shares this vision with modern science. However, the focus of Hinduism has largely been on investigating the nature of consciousness. Several universities in the West have a Centre for Consciousness. This is just the beginning of the singularity in the quest for knowledge, where science and spirituality merge. We need to embrace science but also embrace humanities and spirituality, and ensure that our current and future generations are not a target of scientism that forces one to view science as a dogmatic religion.”
R. Chandra
Nature Human Behaviour, World View (2024)
Evaluation of google translate for Mandarin Chinese translation using sentiment and semantic analysis
Xuechun Wang, Rodney Beard, Rohitash Chandra
Natural Language Processing Journal, Volume 13, December 2025, 100188
Longitudinal abuse and sentiment analysis of Hollywood movie dialogues using language models
Chandra, R., & Ren, G.
Machine Learning with Applications, Volume 22, December 2025, 100749
Unsupervised Machine Learning Framework for Identification of Spatial Distribution of Minerals on Mars
Lovelock, Tejay, and Rohitash Chandra
Remote Sensing 17 (21) (2025) 3578 https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213578
HP-BERT: A framework for longitudinal study of Hinduphobia on social media via language models
Singh, A., & Chandra, R.
IEEE Access, vol. 13, pp. 175309-175335, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3617514
An Evaluation of LLMs and Google Translate for Translation of Selected Indian Languages via Sentiment and Semantic Analyses
R. Chandra, A. Chaudhari and Y. Rayavarapu
IEEE Access, vol. 13, pp. 122386-122407, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3585629
Enigme: Generative Text Puzzles for Evaluating Reasoning in Language Models
John Hawkins
11th ICEAST , Phuket, Thailand, 2025, pp. 117-121, https://doi.org/0.1109/ICEAST64767.2025.11088210.
An Analysis of Vaccine-Related Sentiments on Twitter (X) from Development to Deployment of COVID-19 Vaccines
Rohitash Chandra, Jayesh Sonawane, Jahnavi Lande
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2024, 8(12), 186; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc8120186
Science and Hinduism share the vision of a quest for truth
R. Chandra
Nature Human Behaviour, World View (2024)
Recursive Deep Learning Framework for Forecasting the Decadal World Economic Outlook
Tianyi Wang; Rodney Beard; John Hawkins; Rohitash Chandra
IEEE Access, Volume 12, 2024
Abusive music and song transformation using GenAI and LLMs
Jiyang Choi, Rohitash Chandra
arXiV, 2026. arXiv.2601.15348 [cs.SD]
An evaluation of LLMs for political bias in Western media: Israel-Hamas and Ukraine-Russia wars
Rohitash Chandra, Haoyan Chen, Yaqing Zhang, Jiacheng Chen, Yuting Wu
arXiV, 2026. arXiv:2601.06132 [cs.CY]
Improving AGI Evaluation: A Data Science Perspective
John Hawkins
arXiV, 2025. https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.01687
NLP Methods for Detecting Novel LLM Jailbreaks and Keyword Analysis with BERT
Hawkins, J.; Pramar, A.; Beard, R.; Chandra, R.
arXiV, 2025. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2510.01644
Vedic goddess Sarasvati and the four powers of the mother in Sri Aurobindo’s light
Sushrut Badhe
SSRN, 2025. https://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.5081857
Ensemble quantile-based deep learning framework for streamflow and flood prediction in Australian catchments
Chandra, R., Kapoor, A., Khedkar, S., Ng, J., & Vervoort, R. W.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.15882, 2025.